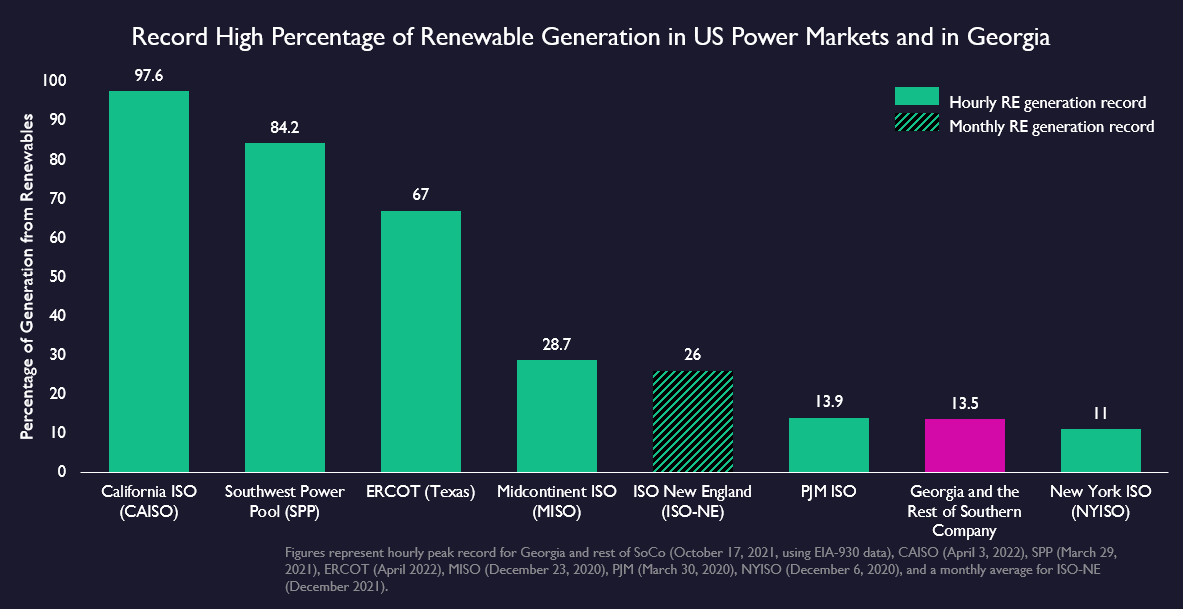
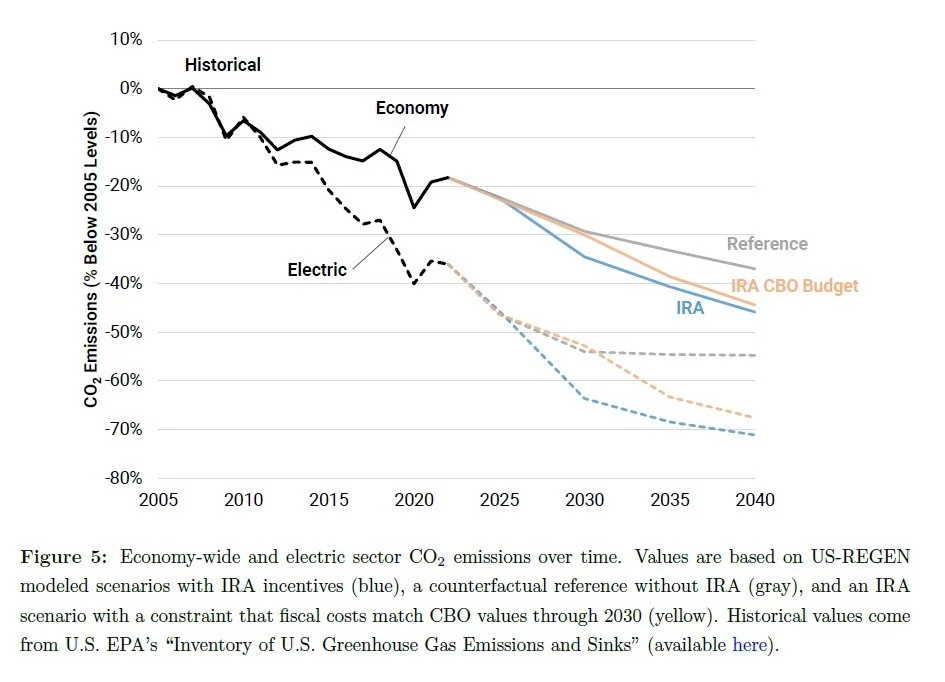
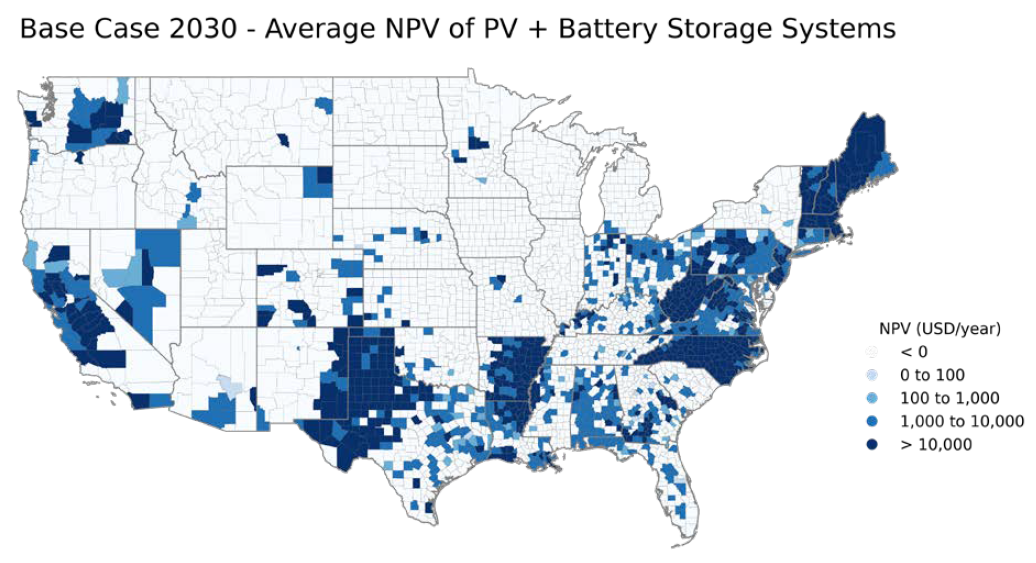
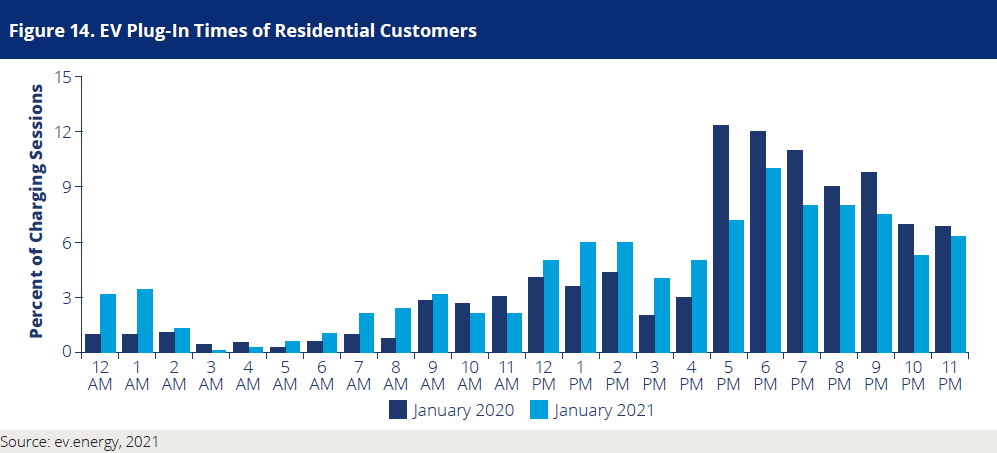
Countless studies support the same conclusion:
We can reliably and resiliently power Georgia’s electric grid with 100% carbon-free renewable energy, nuclear energy, and energy storage. This will lower electricity costs for households and businesses and create new economic activity across all commercial and industrial sectors in Georgia.
Studies on 100% Clean Energy
The Transmission Interconnection Roadmap (PDF) identifies solutions to enable interconnection processes to meet the growing demand for renewable energy resources from the rapid, widespread clean energy transition. Produced by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Interconnection Innovation e-Xchange (i2X) and published in April 2024, this roadmap provides the diverse group of interconnection stakeholders with near- to long-term solutions to address current challenges in transmission system interconnection.
Deploying advanced grid solutions that are available today could cost-effectively increase the capacity of the existing grid to support 20-100 GW of incremental peak demand when installed individually, while improving grid reliability, resilience, and affordability. Solutions such as Reconductoring, Dynamic Line Ratings, Topology Optimization, Advanced Power Flow Control, Energy Storage, and Virtual Power Plants are commercially available today and ready to deploy.
Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE)
Solar PV + Storage - Utility-Scale has a levelized cost of energy of between $46/MWh and $102/MWh, whereas a natural gas peaking technology (combustion turbine) has a levelized cost of energy of between $105/MWh and $229/MWh. The capital cost at the low end ($700/kW) is the same to construct both the Solar PV + Storage - Utility-Scale and the gas peaking plant. Georgia Power Company used this very report to justify building new gas CTs at Plant Yates in the 2023 IRP Update versus Solar PV + Storage - Utility-Scale.
Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS)
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) use cases and applications are becoming more valuable, well understood and, by extension, widespread as grid operators begin adopting methodologies to value BESS resources, which is leading to increased transaction activity and an infrastructure classification for the BESS asset class. Further, while input costs are exposed to the same pressures as the broader Energy Transition sector (e.g., supply chain issues and inflationary pressures), the IRA’s grant of ITC eligibility for standalone BESS assets has kept LCOS values relatively neutral.
2023 April - Brattle & SC General Assembly - Assessment of Potential Market Reforms for South Carolina’s Electricity Sector
This study commissioned by the South Carolina General Assembly finds that a Southeast Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) that shares capacity across geographies would create for state of South Carolina alone up to $187 million in savings each year, and even more if South Carolina joins the pre-existing RTO called PJM. Georgia is 2x the size of South Carolina in terms of population, and the economic benefit of a Southeast RTO would be at least 2x for Georgia, up to $375 million in savings each year for Georgia electricity customers.
2023 March - Brookings Institution - Economic Implications of the Climate Provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act
This report demonstrates with analytical rigor the massive economic benefits of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). It would be folly to reverse the enormous benefits in the name of foregoing the relatively minor costs.
2023 April - How vulnerable are US natural gas pipelines to electric outages?
Gas-electric interdependencies have contributed to several major electric system emergencies. Natural gas pipelines use both gas-powered and electric-powered compressor units; power outages at the latter can cause gas shortages.
Georgia is heavily dependent on natural gas for 50% of its capacity requirements. A full 100% of natural gas is produced outside of Georgia, creating risks, vulnerabilities, and economic dependencies.
2022 January - NREL Storage Futures Study 4th release - Distributed Solar and Storage Outlook
This report examines the potential for behind-the-meter battery storage and identifies key drivers of adoption. BTM batteries along with other Distributed Energy Resources contribute to grid flexibility, reduce grid power losses, and support demand-side management. The market for small-scale battery systems is expected to increase dramatically, pushed by a desire for backup power and the deployment of rooftop solar. FERC Order 2222 will further enable batteries to participate in regional wholesale capacity, energy, and ancillary service markets alongside utility-scale generation. A key insight of this report is that there is significant economic potential for distributed PV + battery storage systems under all modeled scenarios.
2022 January - IEA Wind - Design and Operation of Energy Systems with Large Amounts of Variable Generation
This report brings together experience and study results from 17 collaborating countries and provides detailed findings on:
• incorporating wind and solar generation forecasts within system operations, including grid stability management, and in simulations
• planning for long term adequacy of transmission and generation capacity
• correctly valuing wind and solar energy and capacity in future systems
• dealing with challenges as a system approaches 100% renewable
2021 November - SEPA State of Managed Charging in 2021
There is growing consensus across the transportation and electricity ecosystems that high levels of EV penetration in light-, medium-, and heavy-duty segments are both necessary and inevitable. As society navigates the transition to a low carbon economy and electric vehicles evolve from niche to mainstream, utilities, customers, and vendors will all need to adapt. This report advocates for smart and flexible program design for managed EV charging, capable of evolving as the market evolves.
2021 November - ESIG - Telos Energy - Redefining Resource Adequacy for Modern Power Systems
Comparing the August 2020 California and the February 2021 Texas grid events, this report goes on to define six principles of Resource Adequacy:
Quantifying size, frequency, duration, and timing of capacity shortfalls is critical to finding the right resource solutions.
Chronological operations must be modeled across many weather years.
There is no such thing as perfect capacity.
Load participation fundamentally changes the resource adequacy construct.
Neighboring grids and transmission are a key part of the Resource Adequacy challenge.
Reliability criterion should not be arbitrary, but transparent and economic.
2021 October - World Hydrogen Leaders - Large-scale Electrolysis
This is a very useful round-up of the key sector players in global hydrogen production. The report highlights the need for policy to support the commercial competitiveness of green hydrogen. There is a useful overview of key electrolyser technologies and several case studies of large-scale electrolysers.
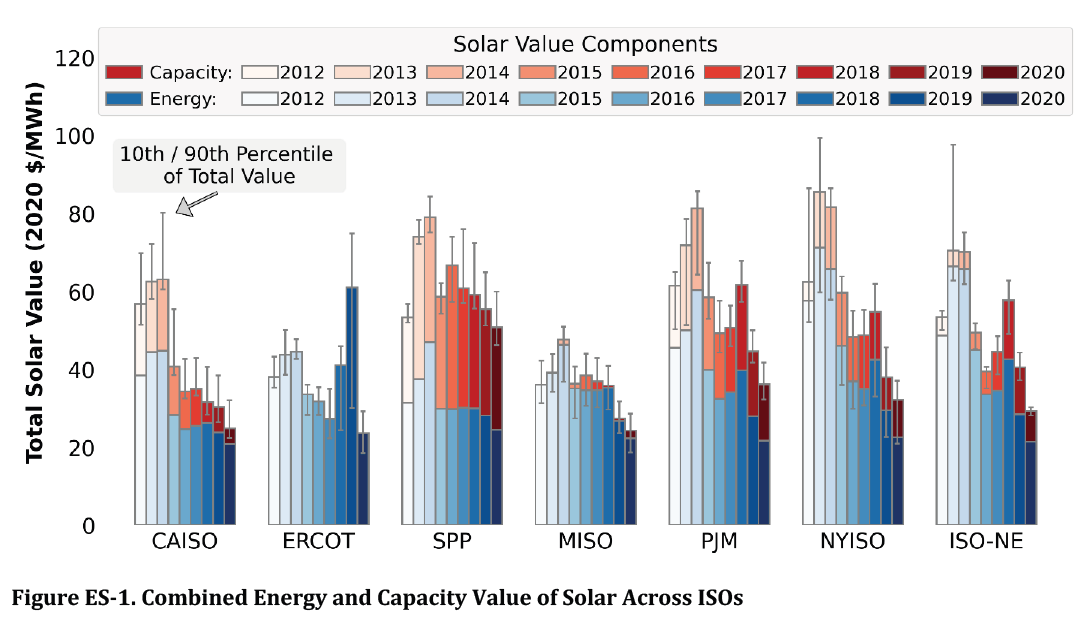
2021 October - Berkeley Lab - Solar-to-Grid: Trends in System Impacts, Reliability, and Market Value in the US
This report focuses on the historical contribution to reliability, trends in market value, and impacts on the bulk power system of solar deployed in the U.S. In particular, Berkeley Lab finds that the bilateral capacity price estimate for solar in the Southeast region (SERC) is as follows:
2012: $78/kW-yr
2013: $47/kW-yr
2014: $49/kW-yr
2015: $66/kW-yr
2016: $55/kW-yr
2017: $61/kW-yr
2018: $32/kW-yr
2019: $46/kW-yr
2020: $14/kW-yr
2021 October - Eastern Interconnection Planning Collaborative - Planning the Grid for a Renewable Future
This industry-led report provides a high-level summary of the challenges that grid operators will encounter as intermittent and energy-limited resources—including renewables—are added to systems. The report also identifies helpful policies. The key takeaway is that each of the apparent challenges can be met with foresight and planning, meaning there are no technical obstacles to achieving a 100% carbon-free electricity grid.
2021 September - NREL Barriers to Community Solar
Solar energy technologies can be used as part of a suite of tools to reduce the energy burden of low-to moderate-income (LMI) households, but to date, LMI customers have not adopted solar at the same rate as other income groups. Income is not the only variable that impacts solar adoption; levels of rooftop PV penetration also differ by race. Community solar and solar on multifamily buildings can also provide solar access pathways to LMI households and households of color.
The study finds that for every dollar spent on partial or full incentives to equip LMI households with solar, those same households would save a dollar in utility bill savings in the first year and for every year thereafter.
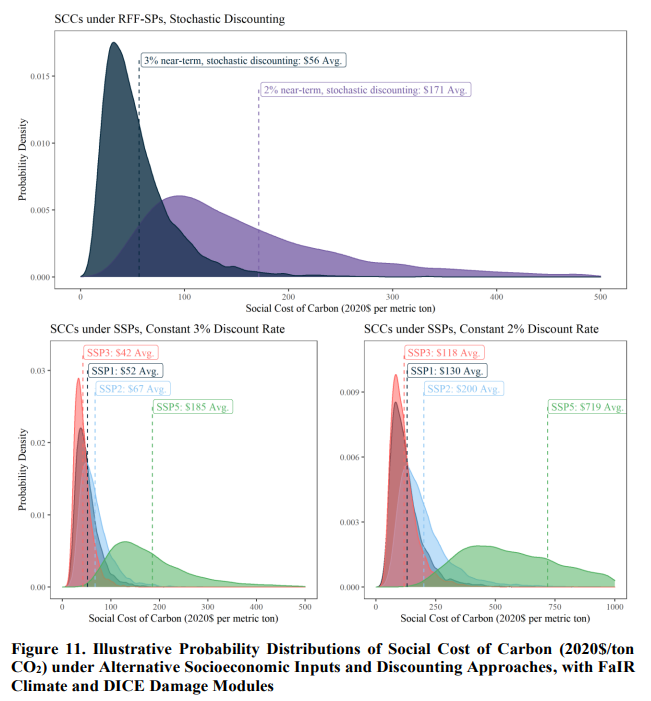
2021 September - Brookings Institution - Social Cost of Carbon
The Social Cost of Carbon (SCC) is a crucial metric for informing climate policy. Characterization of uncertainty and transparency of assumptions are critical for supporting such an influential metric. This study uses probabilistic scenarios to fully characterize the uncertainty distribution and corresponding SCC estimate outputs. Incorporating the full range of economic uncertainty in the SCC underscores the importance of adopting a stochastic discounting approach to account for uncertainty in an integrated manner.
2021 August - SACE/Atlas Public Policy - Transportation Electrification in the Southeast
Across the Southeast, sales of electric vehicles continue to increase but the region lags the national average. The Southeast is home to much activity in the manufacturing of EVs and the EV supply chain. The region is now expected to receive more than 37 percent of all national EV manufacturing investment, up 66 percent from last year. Another 18 percent of all national EV jobs announced, up 33 percent from last year, are also expected to come from manufacturing. Large manufacturing sites continue to open across the Southeast. But stronger supportive policies are needed.
2021 August - Brattle/Cypress Creek - A Pathway to Decarbonization: Generation Cost & Emissions Impact of Proposed North Carolina Energy Legislation
This study finds that Duke Energy could achieve over 70% GHG emissions reductions by 2030 while lowering ratepayer costs by building on the framework of H951 and shifting its resource mix from coal and gas resources to renewable energy and battery storage. Greater GHG emissions reductions could be achieved while decreasing generation costs by $590 million in 2030 and $1,200 million in 2035.
2021 June - Southern Alliance for Clean Energy - Achieving 100% Clean Electricity in the Southeast: Enacting a Federal Clean Electricity Standard
This study demonstrates the overwhelming benefits to ratepayers in the Southeast from an immediate and aggressive push for clean energy resources that exist today (no new technology necessary) like solar and storage. At the time of publishing, Georgia Power Company had plans for a 2035 fleet comprised of 65% fossil generation capacity.
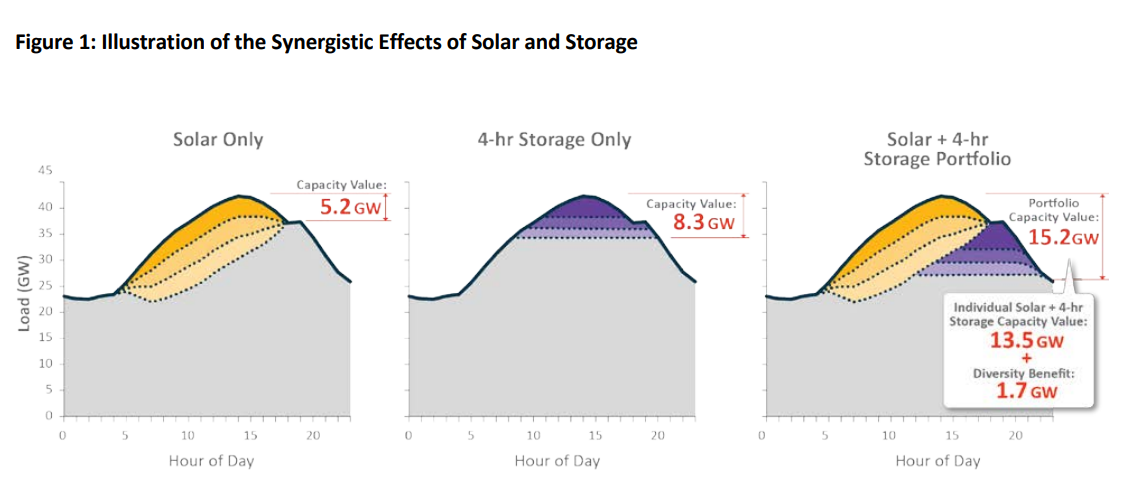
2021 June - Sodano et. al (NCSU) - The symbiotic relationship of solar power and energy storage in providing capacity value
Ensuring power system reliability under high penetrations of variable renewable energy is a critical task for system operators. Using a loss of load probability model to estimate the capacity credit of solar PV and energy storage under increasing penetrations of both technologies, in isolation and in tandem, to offer new understanding on their potential synergistic effects.
The study finds that solar PV and storage used together make a more significant contribution to system reliability: as much as 40% more of the combined capacity can be counted on during peak demand hours compared to scenarios where the two technologies are deployed separately.
These findings are timely as utilities replace their aging peaking plants and are taking energy storage into consideration as part of a low carbon pathway.
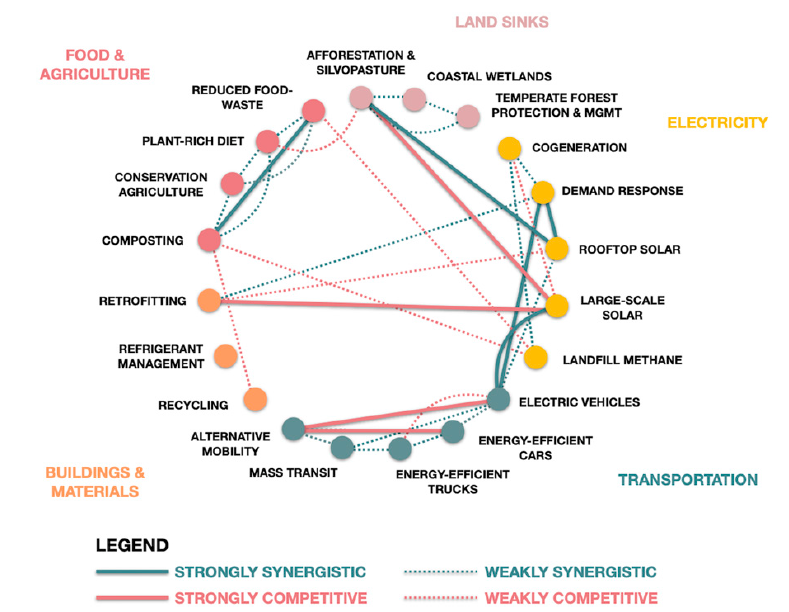
2021 May - Georgia Technology of Institute - A Framework for Localizing Global Climate Solutions and Their Carbon Reduction Potential
Georgia is a state that lacks any kind of climate leadership from the Governor’s Office to the Public Service Commission. The researchers identified 20 solutions that could cut Georgia greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2030 compared to 2005. Many of these solutions would create new wealth (net positive benefits) based not only on economics but from the co-benefits of mitigating climate impacts on public health, environmental quality, employment, and equity.
2021 April - Southern Alliance for Clean Energy - Tracking Decarbonization in the Southeast (Generation + CO2 Emissions Report)
Southern Company is not close to being on track to meet its net-zero goal by 2050. Historical reductions have been much sharper than reductions that the collective Integrated Resource Plan [of the Operating Companies including Georgia Power Company] will yield over the next decade. However, both fall short of meaningful reductions that would allow the company to reach zero by 2050. In particular, Georgia Power Company missed cues from its parent company and the City of Atlanta, which adopted a 100% clean energy goal.
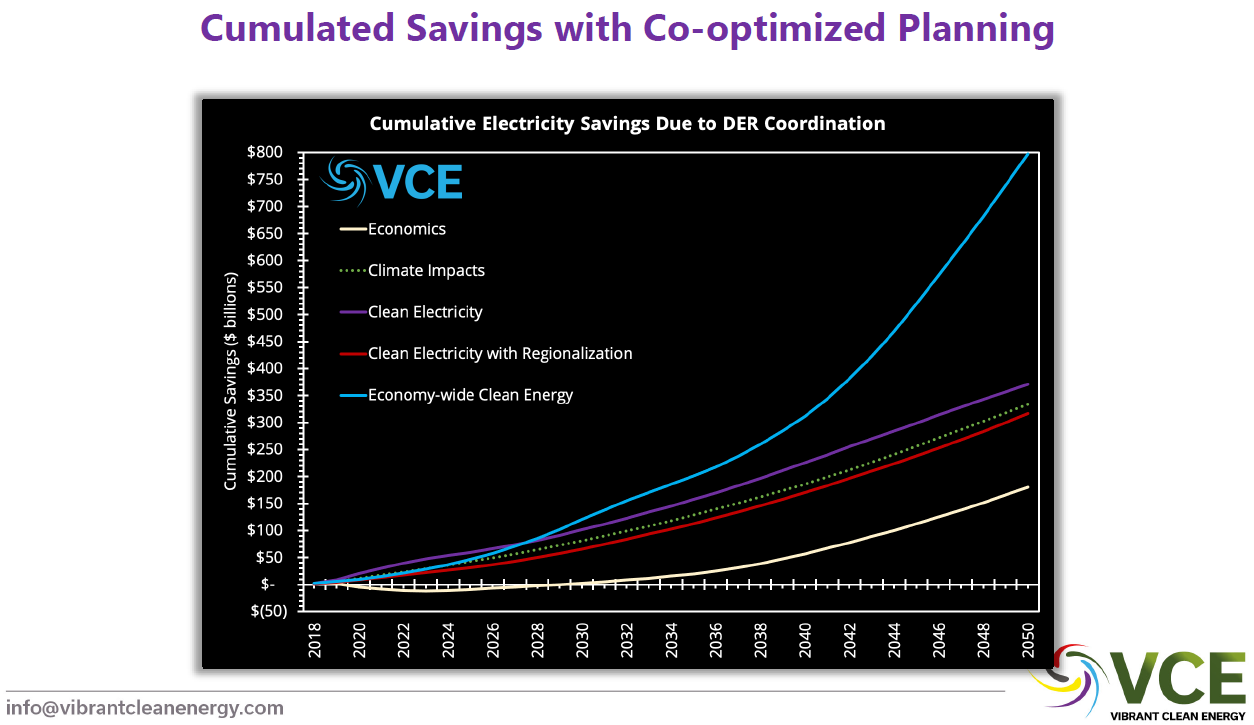
2021 April - Vibrant Clean Energy - Co-Optimization Techniques and Results of Planning Generation and Transmission Together
Dr. Christopher Clack and team demonstrate on the national level that the cumulative electricity savings from coordinating Distributed Energy Resources (DER) together with traditional utility Integrated Resource Planning (which focuses principally on generation within a balancing area or larger market area, but with limited transmission optimization) can lead to enormous economic benefits. In fact, planning for DERs and ensuring they receive fair market participation remuneration could lead to cumulative savings of $800 billion dollars nationwide by 2050. In Georgia, the primary impediment to unlocking these savings is Georgia Power Company and the monopoly utility model.
2021 March - Ampacimon - Dynamic Line Rating: How PPL is lifting congestion costs in the PJM region
In this case study, Ampacimon describes how PPL mitigated an estimated $14.5 million in annual congestion costs in 2025 on one of its 230 kV transmission lines in PJM. It considered three solutions, selecting Dynamic Line Rating (DLR) as the best option. 12 DLR sensors were installed for <$1 million, resulting in an increase of 29% transmission capacity in the summer and 25% more transmission capacity in the winter.
2021 March - Aarhus University (Denmark) et al. - Solar Photovoltaic Energy is Ready to Power a Sustainable Future
Solar photovoltaics are today a highly cost-competitive technology, ready to contribute substantially to CO2 emissions mitigation. However, many scenarios and models fail to identify the key role that this technology could play, including far lower future PV capacity than that projected by the PV community. In this paper, the authors aim at open a constructive discussion among PV experts, modelers, and policymakers regarding how to improve the representation of this technology in the models and how to ensure that manufacturing and installation of solar PV- can ramp up on.